Our approach advocates an iterative two-step learning-based paradigm:
To start with, an initial partial segmentation of the filamentary structure is obtained using the existing segmenter.
Step one of our approach centers on a data-driven latent classification tree model to detect the foreground filamentary fragments.
This model is learned via a training process, where a large number of distinct local figure/background separation scenarios
are established and geometrically organized into a tree structure.
Step two spatially restores the isolated fragments back to the current partial segmentation,
which is accomplished by means of completion fields and matting.
Both steps are then alternated with the growth of partial segmentation result, until the input image space is entirely explored.
Our approach is rather generic and can be easily augmented to a wide range of existing supervised/unsupervised segmenters to produce an improved result.
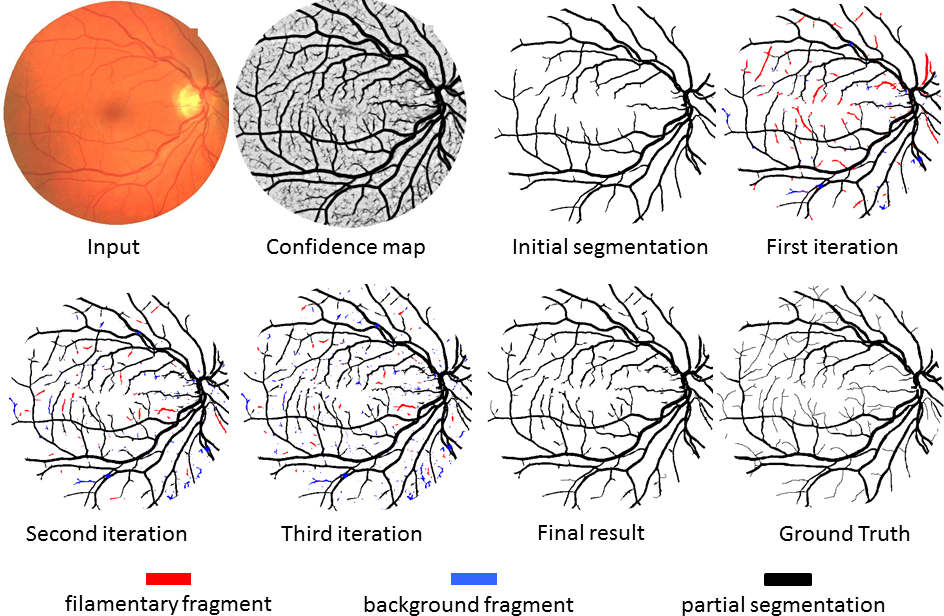
Top row: Input image; The confidence map from a base segmenter; Initial partial segmentation obtained by applying a sufficiently high
threshold in the confidence map; First iteration result.
Bottom row: 2nd & 3rd iteration results; Final result, in comparison with the ground truth.
|